Location Planning
Every firm must use location planning techniques.
There are many options for location planning. Corporations choose from
expanding an existing location, shutting down one location and moving to
another, adding new locations while retaining existing facilities, or doing
nothing. There are a variety of methods used to decide the best location or
alternatives for the corporation. Methods such as identifying the country, general
region.
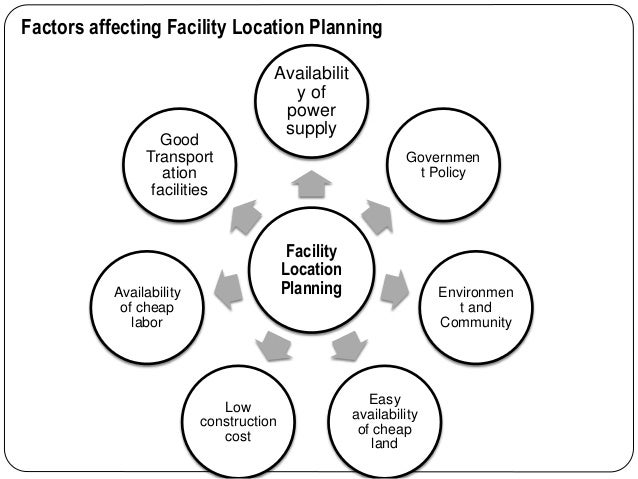
Several factors that influence location positioning include the location of raw materials, proximity to the market, climate, and culture. Models for evaluating whether a location is best for an organization consist of cost-profit analysis for locations, the centre of gravity model, the transportation model, and factor rating.
Several factors that influence location positioning include the location of raw materials, proximity to the market, climate, and culture. Models for evaluating whether a location is best for an organization consist of cost-profit analysis for locations, the centre of gravity model, the transportation model, and factor rating.
The main factors that affect location decisions
include regional factors, community considerations, and site-related factors.
Community factors consist of quality of life, services, attitudes, taxes,
environmental regulations, utilities, and development support.
IDENTIFYING REGION- 4 major considerations
·
Location to Raw
Materials: The three most important reasons for a
firm to locate in a particular region include raw
materials, perishability, and transportation cost. This often depends on what business the
firm is in.
·
Location to Markets: Profit
maximizing firms locate near markets that they want to serve as part of their
competitive strategy. A Geographic
information system (GIS) is
a computer based tools for collecting, storing, retrieving, and displaying
demographic data on maps.
·
Labour Factors: Primary considerations include labour
availability, wage rates, productivity, attitudes towards work, and the impact
unions may have.
·
Other: Climate is sometimes a consideration because bad weather can
disrupt operations. Taxes are also an important factor due to the fact that
taxes affect the bottom line in some financial statements.
IDENTIFYING
A SITE
The main considerations in choosing a site are
land, transportation, zoning and many others. When identifying a site it is
important to consider to see if the company plans on growing at this location.
If so, the firm must consider whether or not location is suitable for
expansion. There are many
decisions that go into choosing exactly where a firm will establish its
operations. First, a company must determine the driving factors that will
influence which areas are suitable locations. After these factors have been
determined, the company will identify potential countries and examine the pros
and cons of establishing operations in these countries. After looking at pro
and cons of the different countries and deciding on a country, then decision
makers will identify a region within the country. When identifying a region,
decision makers must take the four major factors explained above into
consideration. The last two stages of the search include choosing a community
and a site.
Method
used for calculating the location of the Distribution Centre and the regional
warehouses-
Centre of Gravity Method:
This technique is used in determining
the location of a facility which will either reduce travel time or lower
shipping costs. Distribution cost is seen as a linear function of the distance
and quantity shipped. The Centre of Gravity Method involves the use of a visual
map and a coordinate system; the coordinate points being treated as the set of
numerical values when calculating averages. If the quantities shipped to each
location are equal, the centre
of gravity is found by taking the averages of the x and y coordinates;
if the quantities shipped to each location are different , a weighted average must be applied (the weights
being the quantities shipped)
Calculation:
1.
Calculation of No of items in shipment:
The semi-trailers can hold up to 33
pallets
Each pallet can hold how many cartons:
One Pallets dimension =800 x 1200 Cm
One carton will be occupying an area
of =60 x 40 Cm
Therefore, the no: of cartons loaded
(as in first layer) =800 x 1200/(60 x
40) =400 Cartons
No: of layers (wrt height) = 240/30= 8
layers
No: of cartons in
semitrailers(shipped)= 400 x 8 x 33 = 105600 Cartons
There are 4 warehouses for 4
respective factories
so
the actual cartons shipped = 4 x 105600=422400 Cartons
2.
Items in Circulation:
No
of items in circulation= regional + shipped
There
are 4 regional warehouse for each factory, so the no: of items in circulation
for each factory =4 x 500=20000
For
4 factories =20000 x 4= 80000
.:
the total items in circulation = 422400+80000=502400
Assumptions:
1. The Demands for one particular date 01-2019
04-is considered.
2. The demands of all the customers are met.
3. The regional warehouses are located near the
place where there is more demand
4. If the city with more demand is met, then the
demand in the surrounding places can be met accordingly.
5. The values applied on demand are approximated
to some degree.
Lorsch
Each
central warehouse need to meet 82678 items/month.
Buttenheim: 1794/500= 4 trucks
Hamburg: 1776/500= 4 trucks
Berlin: 1608/500= 4 trucks
Köln: 1191/500= 3 trucks
Mannheim
Each
central warehouse need to meet 172159 items/month.
Mönchengladbach: 5823/500= 12 trucks
Lüdwigshafen: 1447/500= 3 trucks
Braunswick: 1456/500= 3 trucks
Berlin:
1696= 4 trucks
Vechta
Each
central warehouse need to meet 63154 items/month.
Köln: 1395/500= 3 trucks
Hamburg: 1382= 3 trucks
Frankfurt am Main: 483= 1 truck
Dresden= 143/500= 1 Truck
Mönchengladbach
Each
central warehouse need to meet 276286 items/month.
Köln: 13912/500= 28 trucks
München: 3475/500= 7 trucks
Berlin: 3524/ 500= 8 trucks
Hamburg:
5409/500= 11 trucks
S.No
|
Central Warehouse
|
Regional Warehouse
|
Percentage demand/
regional Warehouse
|
Trucks needed per
Regional warehouse
|
1
|
Lorsch
|
Büttenheim
|
49.2
|
4
|
Berlin
|
27.8
|
4
|
||
Hamburg
|
25.2
|
4
|
||
Köln
|
18.7
|
3
|
||
2
|
Mannheim
|
Mönchengladbach
|
55.8
|
12
|
Lüdwigshafen
|
13.8
|
3
|
||
Brunswick
|
13.9
|
3
|
||
Berlin
|
16.2
|
4
|
||
3
|
Vechta
|
Köln
|
48.8
|
3
|
Hamburg
|
43.3
|
3
|
||
Frankfurt am
Main
|
15.1
|
1
|
||
Dresden
|
4.4
|
1
|
||
4
|
Mönchengladbach
|
Köln
|
52.8
|
28
|
München
|
13.2
|
7
|
||
Berlin
|
13.3
|
8
|
||
Hamburg
|
20.5
|
11
|
The no: of items in circulation:
The No. of items in circulation for a
single day (04-01-2019) is calculated,
S.No
|
Central Warehouse
|
Demand on the selected day
|
1
|
Lorsch
|
1200
|
2
|
Mannheim
|
7181
|
3
|
Vechta
|
4500
|
4
|
Mönchengladbach
|
13431
|
Locations:
The location of the customers,
location of the factory, location of the central warehouse and location of the
regional warehouses are calculated according the given Longitudinal and
Latitudinal positions and they are marked in Google maps for better
understanding and reference.
Locations of the Factories:
S. No
|
Representation of the factories
|
Latitudinal value
|
Longitudinal Value
|
1
|
Mannheim
|
49.494034128078000
|
8.45711420315853
|
2
|
Lorsch
|
49.6409044696465000
|
8.56493556447512
|
3
|
Mönchengladbach
|
51.1963658241177000
|
6.43379455120694
|
4
|
Vechta
|
52.7428116120401000
|
8.2836006861168300
|
Location of the Central Warehouses:
Sample Calculation for Central Warehouse
location for Lorsch:
Total Sum of Demand = 82678
∑ Lat X Demand = 4207211.115
∑ Long X Demand = 782148.4652
Lat for Central Warehouse (x)
=782148.4652/82678 = 9.46017641
Long for Central Warehouse (y) =
4207211.115/82678= 50.8867064
S. No
|
Representation of the
Central warehouses
|
Latitudinal value
|
Longitudinal Value
|
1
|
Mannheim
|
50.16541035
|
7.742670888
|
2
|
Lorsch
|
50.8867643
|
9,46017641
|
3
|
Vechta
|
50.07490742
|
7.924501258
|
4
|
Mönchengladbach
|
51.0761371,
|
7.981192811
|
Location of the regional warehouses:
Lorsch
S.No
|
Representation of the Regional
Warehouses
|
Latitudinal value
|
Longitudinal Value
|
1
|
Buttenheim
|
49.82950824
|
11.07254563
|
2
|
Berlin
|
52.5729887447053000
|
13.443301207034300
|
3
|
Hamburg
|
53.5878682327500
|
9.734921306135
|
4
|
Köln
|
50.92480502
|
6.950127682
|
Vechta:
S.No
|
Representation of the Regional
Warehouses
|
Latitudinal value
|
Longitudinal Value
|
1
|
Frankfurt am main
|
50.0238419217
|
8.84232127
|
2
|
Dresden
|
51.009786542
|
13.31715272
|
3
|
Hamburg
|
53.572472791
|
10.151723147
|
4
|
Köln
|
50.8724347619
|
6.8714321719
|
Mannheim:
S. No.
|
Representation of Regional
Warehouse
|
Latitude
|
Longitude
|
1.
|
Mönchengladbach
|
51.203457971
|
6.741327154
|
2.
|
Lüdwigshafen
|
49.497254721
|
|
3.
|
Braunschweig
|
52.2864327
|
10.433217900
|
4.
|
Berlin
|
52.427134171
|
13.541297524
|
Mönchengladbach:
S. No.
|
Representation of Regional
Warehouse
|
Latitude
|
Longitude
|
1.
|
Köln
|
50.8724347619
|
6.8714321719
|
2.
|
Hamburg
|
53.572472791
|
10.151723147
|
3.
|
Frankfurt
|
50.0238419217
|
8.81232127
|
4.
|
Dresden
|
51.009786542
|
13.31715272
|
Comments
Post a Comment